Difference between revisions of "References"
m |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | <span style="color:#0000FF; font-size: 200%;">Please share references by adding links | + | <span style="color:#0000FF; font-size: 200%;"><u>Please share references by adding links into this page</u></span> |
</center> | </center> | ||
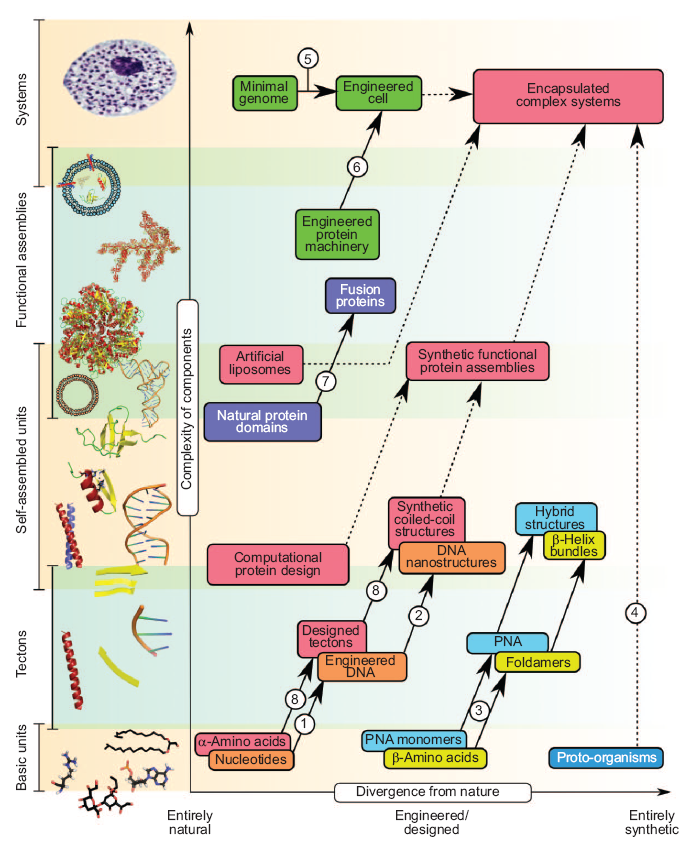
| + | [[Image:route.png|thumb|ACS Chem. Biol., 2008, 3 (1), pp 38–50|right|300px]] | ||
== General Principles of Synthetic Biology == | == General Principles of Synthetic Biology == | ||
[http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v438/n7067/abs/nature04335.html Reconstruction of genetic circuits] | [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v438/n7067/abs/nature04335.html Reconstruction of genetic circuits] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6VRV-4KPX8RY-1&_user=126524&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000010360&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=126524&md5=32f32f9adee8425380015b935a6eadf8 Systems biology as a foundation for genome-scale synthetic biology] | [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6VRV-4KPX8RY-1&_user=126524&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000010360&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=126524&md5=32f32f9adee8425380015b935a6eadf8 Systems biology as a foundation for genome-scale synthetic biology] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v469/n7329/full/469171a.html Synthetic biology: Division of logic labour] Cellular compartmentalization is an effective way to build gene circuits capable of complex logic operations, in which binary inputs are converted into binary outputs according to user-defined rules. | ||
== Parts Standardization/Construction == | == Parts Standardization/Construction == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
[http://www.nature.com/msb/journal/v4/n1/full/msb200824.html A synthetic Escherichia coli predator–prey ecosystem] | [http://www.nature.com/msb/journal/v4/n1/full/msb200824.html A synthetic Escherichia coli predator–prey ecosystem] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v434/n7037/full/nature03461.html A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation] | ||
== Software Packages/Tools == | == Software Packages/Tools == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 46: | ||
== Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (ELSI) == | == Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (ELSI) == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v468/n7326/pdf/468889a.pdf Build life to understand it] Biologists and engineers should work together: synthetic biology reveals how organisms develop and function, argue Michael Elowitz and Wendell A. Lim. | ||
| + | |||
[http://www.synbiosafe.eu/uploads///pdf/Diffusion_of_synthetic_biology.pdf Diffusion of synthetic biology: a challenge to biosafety. Systems and Synthic Biology] | [http://www.synbiosafe.eu/uploads///pdf/Diffusion_of_synthetic_biology.pdf Diffusion of synthetic biology: a challenge to biosafety. Systems and Synthic Biology] | ||
[http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/summary/286/5447/2087 Ethical Considerations in Synthesizing a Minimal Genome] | [http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/summary/286/5447/2087 Ethical Considerations in Synthesizing a Minimal Genome] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 13 January 2011
Please share references by adding links into this page
General Principles of Synthetic Biology
Reconstruction of genetic circuits
Engineering life: building a fab for biology
Engineering life through Synthetic Biology
Systems biology as a foundation for genome-scale synthetic biology
Synthetic biology: Division of logic labour Cellular compartmentalization is an effective way to build gene circuits capable of complex logic operations, in which binary inputs are converted into binary outputs according to user-defined rules.
Parts Standardization/Construction
Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices
Engineering BioBrick vectors from BioBrick parts
Mathematical/Computational Methods
Sensitivity and robustness in chemical reaction networks
New Designs/Design Principles
A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators
The incoherent feed-forward loop can generate non-monotonic input functions for genes
In-vivo/vitro Chassis
Protein synthesis by pure translation systems
Principles of cell-free genetic circuit assembly
Applications
A synthetic Escherichia coli predator–prey ecosystem
A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation
Software Packages/Tools
Measurement Methods
Single-cell analysis of gene expression by fluorescence microscopy
Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (ELSI)
Build life to understand it Biologists and engineers should work together: synthetic biology reveals how organisms develop and function, argue Michael Elowitz and Wendell A. Lim.
Diffusion of synthetic biology: a challenge to biosafety. Systems and Synthic Biology